Since the early 1990’s – when the concept of data warehousing started, the IT sector witnessed some major changes.
The rapid evolution of Business Intelligence over the past few years has drastically changed the way organizations collect, store, evaluate and analyze data.
But before going any further it’s essential to understand what exactly “Business Intelligence” (BI) means.
According to Howard Dresner, BI can be referred to as an umbrella term to describe “concepts and methods to improve business decision-making by using fact-based support systems.”
Traditionally, BI systems were used just by the IT department. Employees from all types of departments used to barge the IT staff with requests regarding the required data.
The concerned IT employee (who unusually tends to be familiar with all sorts of data) then extracts data from the BI system and uses Excel or a related software to prepare a report of the user’s choice.
This type of approach has had many disadvantages such as:
- The IT department was flooded with requests, leaving no time for them to concentrate on pressing issues.
- Employees hover around the IT department for hours only to get some new data but not a fresh report.
- Since the data was siloed, delivering data to decision-makers took a longer time.
The New Age BI: Business Intelligence 2.0
Over the past few years, BI tools underwent radical changes.
Employees don’t need to waste their valuable time waiting for the IT department.
They can get the most recent and updated data, insights, and advanced visualization features like charts, graphs, dynamic 3D maps, etc. and dashboards.
The most incredible aspect of self-service BI tools is that they need minimal technical knowledge for usage.
With these tools, users can now access all the internal and external data from various sources and even project it in numerous ways.
All these procedures can be carried out hassle-free with the basic tech skills
Your IT staff can finally take a deep breath and concentrate on more productive work.
The primary goal of a self-service BI is to give Business executives the power to quickly access the data they need and generate an easy-to-understand report with dynamic visualizations.
As of today, Power BI and Tableau’s BI remain the top emerging players in this arena.
The rapid growth of the Internet also played a vital factor in the success of BI 2.0. The advent of social media channels, blogs, etc. led users to share their ideas and opinions instantly.
Here Are Some Key Characteristics and Advantages of a Self-Service BI:
- Reports can be accessed through multiple devices and platforms. It is also very easy to deploy a self-service BI on various channels.
- The total costs for ownership and change ( TCO & TCC) of a self-service BI are comparatively lower than those of a traditional BI.
- If the audience is business users, they need customized report dashboards and templates to complete ad hoc queries. Self-service BI tools help users in:
- Generating accurate and template based reports
- Suggesting data elements in a particular row or column
- Enabling a text search interface to users during the selection of different attributes
- Creating advanced analysis
- Data discovery, extraction, and processing are extremely quick and organized, enabling employees to get their questions answered fast and smooth.
- A self-service BI typically has a higher adoption rate compared to a traditional one as a self-service BI won’t require users to code or have deep technical knowledge.
- An effective BI tool can even present you the actual cause & solution to the required business problem within few seconds.
The “Power” of Power BI
Since it’s launch in July 2015, Power BI is constantly updated by Microsoft with fresh features every month. In February 2017, Gartner even awarded Microsoft the top leadership position in its Magic Quadrant for Business Intelligence and Analytics Platforms.
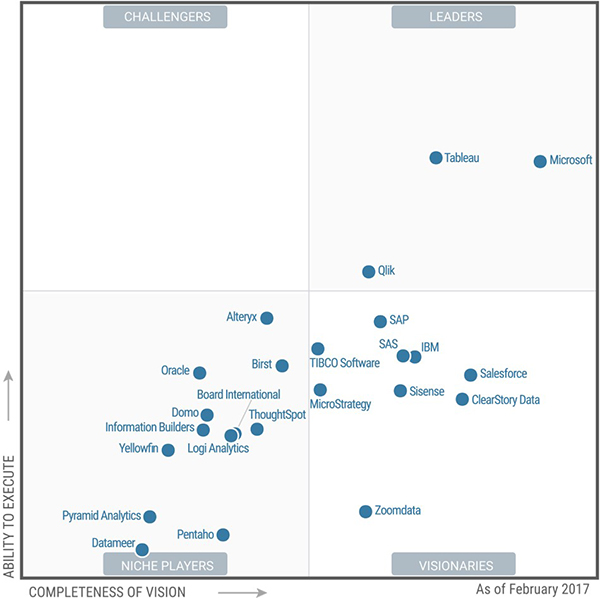
The competition among BI software in the global market has become extremely cut throat in the past few years. Vendors are now competing over the most narrow differences.
As of May 2017, Microsoft launched some important and promising updates to Power BI which can take the adoption of a self-service BI to the next level.
Some noteworthy updates include:
- Connecting to data sets in the Power BI service
- Quick measure update to swiftly perform common and powerful calculations. Through this update, even users with the least knowledge about Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) can perform vigorous calculations hasslefree.
- The launch of Power BI apps (preview version). Through these apps, organizations can now deploy purpose-built dashboards and reports and any business user who has the access to a particular app can make data-driven decisions accordingly.
Further Reading…
https://powerbi.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/power-bi-desktop-may-feature-summary/
Along with these updates, Power BI also has a Q&A based natural language interface which makes the software extremely easy to use.
Another important use case of Power BI is that easily connects with third-party cloud data sources like Salesforce, Google Analytics, Marketo etc.
This continuous updating of Power BI with the latest features has helped Microsoft stay ahead in the global self-service BI software market.
The Future of Self-Service BI
Many industries such as Healthcare, Banking, Retail etc have recognized the importance of a Self-service BI and are adopting it rapidly. As the need for scaling of BI is growing, cloud-based data warehouses are going to gain a lot of popularity.
As the BI tools continue to become more useful and less sophisticated for an average user, the role of the in-house IT department in the future is something to watch out for.
Though BI tools look flashy, an organization might need the IT department to store and secure the data that needs to be analyzed.
What’s your take on the future of Self-service BI? Leave a comment below and let us know your thoughts…



